
 BACKGROUND:
BACKGROUND:
Approximately 1/3 of bronchiectasis patients become chronically infected with the opportunistic bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). This pathogen effectively evades killing by immune cells and forms protective biofilms which result in persistent infections that can become resistant to antibiotics. Consequently, P. aeruginosa infection is associated with worsened clinical outcomes and reduced quality of life in bronchiectasis.
Treatment options for P. aeruginosa are inadequate and antibiotic current antibiotic treatments are also not pathogen-specific, meaning they disrupt the overall diversity of the airway microbiome.
As such, there is an urgent need for novel anti-pseudomonal treatments, particularly those that are pathogen-specific.
TRIAL OVERVIEW:
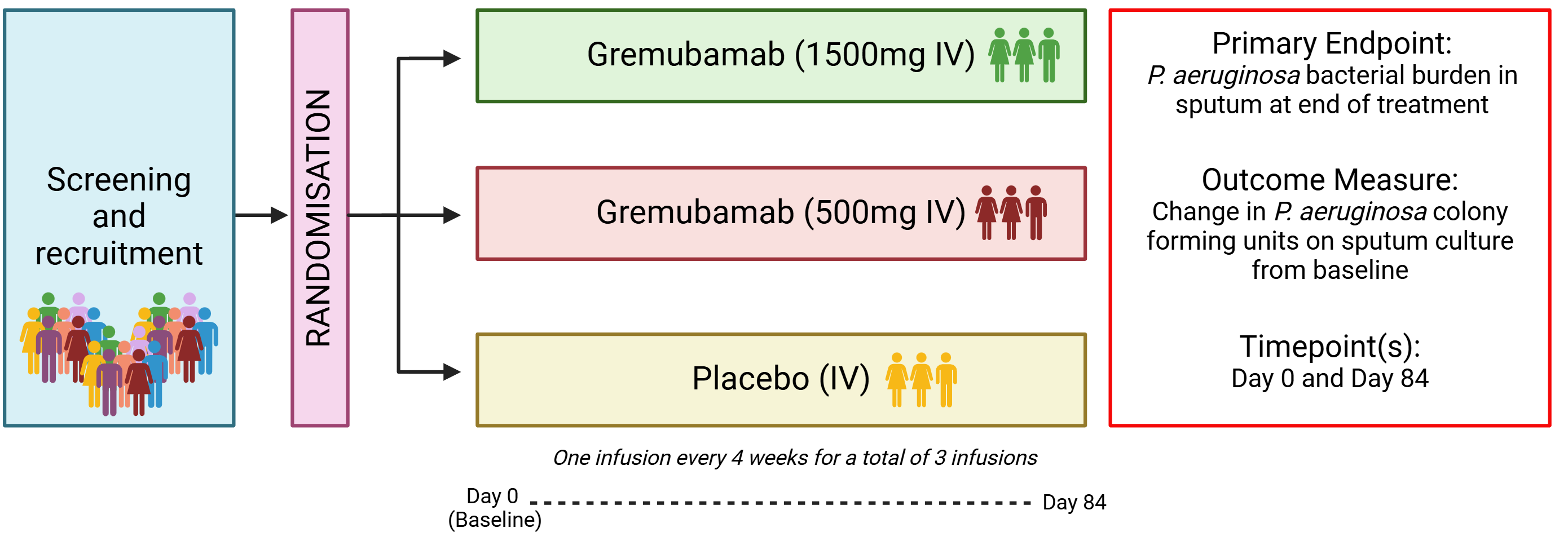
GREAT-2 is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial testing Gremubamab – an intravenous anti-pseudomonal bispecific monoclonal antibody drug – in patients with bronchiectasis chronically infected with P. aeruginosa.
The drug works by binding to PcrV, a component of the Type 3 secretion system Pseudomonas uses to release virulence factors, and Psl, an exopolysaccharide involved in immune evasion, biofilm formation, and cell attachment, thus preventing their function.
Gremubamab has previously been shown to increase neutrophil-mediated killing of P. aeruginosa in neutrophils isolated from bronchiectasis patients, resulting in comparable bacterial killing with neutrophils from healthy control subjects, in a proof-of-concept study.
The GREAT-2 trial aims to:
- Establish the anti-pseudomonal activity of Gremubamab in-vivo
- Determine the optimal dosing of Gremubamab (1500mg or 500mg)
- Provide preliminary evidence of the clinical efficacy of Gremubamab in those with bronchiectasis, including the effect of the drug on exacerbations and patient quality of life.
 The GREAT-2 Trial is managed by the Tayside Clinical Trials Unit (TCTU).
The GREAT-2 Trial is managed by the Tayside Clinical Trials Unit (TCTU).
For further information on the trial, including essential trial documentation and training resources, please visit:
https://sites.dundee.ac.uk/great-2/
Please note, recruitment to this trial has now ended.
The following sites participated in the trial:
- Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee
- Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham
- Royal Brompton Hospital, London
- University Hospital Llandough, Llandough
- Royal Papworth Hospital, Cambridge
- Hammersmith Hospital, London
- Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Exeter
- The Princess Alexandra Hospital, Harlow
- Belfast City Hospital, Belfast
- Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester
- Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
- Northwick Park Hospital, Harrow
- Hospital Clinic, Barcelona
- Hospital Trueta, Girona
- Hospital German Trias, Badalona
- Hospital Universitario Son Espases, Palma
- Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge, Barcelona
- Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona
